华南理工大学物理与光电学院,广东 广州 510641
反手性拓扑光子态是具有抗背向散射及免疫缺陷特性的新型波导态,其在拓扑光子晶体的两个平行边界沿相同方向单向传输,在拓扑激光、集成光路、量子信息等领域展示出应用潜力。本文聚焦反手性拓扑光子态研究进展,从Dirac模型出发,推演经典Haldane模型、反手性Haldane模型以及异质Haldane模型,并展示不同拓扑态的传输行为。讨论手性边界态、反手性边界态以及单向体态在光子晶体中的实现,重点介绍基于反手性拓扑光子态的紧凑单向波导、拓扑环形腔、拓扑分束器等拓扑光学器件。最后针对反手性拓扑光子态研究面临的关键问题、未来发展趋势进行分析和展望。
反手性拓扑光子态 单向传输 拓扑光子晶体 拓扑器件 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(15): 1500001
1 福州大学晋江科教园区海洋工程研发中心,晋江 362200
2 福州大学生物科学与工程学院,福州 350108
3 福州大学天然产物与中药现代化研究所,福州 350108
以天然植物组织油茶粕为原料, 通过水提法制备绿色发泡剂, 并采用物理发泡方式制备泡沫混凝土, 研究混泡时间、水胶比和泡沫掺量对泡沫混凝土干密度、抗压强度及孔结构的影响。结果表明: 绿色发泡剂泡沫稳定性高, 可用于制备低密度泡沫混凝土, 是一种优质的新型绿色发泡剂; 当泡沫掺量为750 mL、混泡时间为180 s、水胶比为0.45时, 所制备的A05密度等级泡沫混凝土的吸水率为45%, 抗压强度为1.52 MPa, 并且绿色发泡剂制备的泡沫混凝土孔径分布均匀, 孔径小(最大气孔孔径dmax<0.6 mm), 气孔形态完整。
油茶粕 绿色发泡剂 泡沫混凝土 物理发泡 微观孔结构 孔径分布 camellia meal green foaming agent foam concrete physical foaming microscopic pore structure pore size distribution

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
We propose a pseudospin-field-dependent waveguide (PFDW) by constructing a sandwiched heterostructure consisting of three magneto-optical photonic crystals (MOPCs) with different geometric parameters. The upper expanded MOPC applied with an external magnetic field has broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) and an analogous quantum spin Hall (QSH) effect, while the middle standard and the lower compressed ones are not magnetized and trivial. Attributed to the TRS-broken-QSH effect of the upper MOPC, the topological large-area one-way transmission that uniformly distributes over the middle domain is achieved and exhibits the characteristics of a pseudospin-field-momentum-locking; i.e., pseudospin-down (or pseudospin-up) leftward (or rightward) waveguide state when the positive (or negative) magnetic field is applied on the upper MOPC. We further demonstrate the strong robustness of the PFDW against backscattering from various kinds of defects. In addition, a topological beam modulator that can compress or expand the light beam, and a large-area pseudospin beam splitter have been designed. These results have potential in various applications such as sensing, signal processing, and optical communications.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(6): 1105
1 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所中国科学院大气光学重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230031
2 中国科学技术大学 研究生院科学岛分院,安徽 合肥 230026
3 先进激光技术安徽省实验室,安徽 合肥 230037
为了实现高精度连续探测对流层和平流层大气风场,搭建了一台直接测风激光雷达系统对对流层和平流层大气风场进行探测。该系统基于双边缘法布里-珀罗标准具的瑞利散射多普勒测风原理,使用转台式探测结构,通过频率跟踪的手段对频率漂移进行跟踪,确保测风的精度。实验结果表明,该系统对对流层和平流层大气风场探测效果良好,频率跟踪的范围为±50 MHz,可以大大减小频率漂移带来的风速误差。经过系统的稳定运行和长时间的观测,在40 km处测得的径向风速随机误差为8 m/s。径向风速合成为水平风速后,随机误差在38 km处最大为10 m/s左右。该系统白天探测高度为25 km,夜晚探测高度为38 km。与探空数据对比,风速误差均小于10 m/s,其中风速误差在±5 m/s的范围内的数据量约占75.8%,探测的风向误差与探空气球的趋势基本一致,误差范围在10°~20°之间,在15°范围内的数据量约占58.6%。将实测数据与探空数据进行统计分析,结果具有良好的一致性。该系统可以为对流层和平流层大气风场的探测提供数据支撑。
直接测风激光雷达 大气风场 法布里-珀罗干涉仪 瑞利散射 direct wind lidar atmosphere wind field Fabry-Perot interferometer Rayleigh scattering 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(2): 20220412

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
![]()
![]() Antichiral gyromagnetic photonic crystal (GPC) in a honeycomb lattice with the two interpenetrating triangular sublattices A and B magnetically biased in opposite directions can realize antichiral one-way edge states propagating along the same direction at its two parallel edges. Here, we report the construction and observation of topological beam splitting with the easily adjustable right-to-left ratio in an antichiral GPC. The splitter is compact and configurable, has high transmission efficiency, and allows for multi-channel utilization, crosstalk-proof, and robust against defects and obstacles. This magnificent performance is attributed to the peculiar property that antichiral one-way edge states exist only at zigzag edge but not at armchair edge of antichiral GPC. When we combine two rectangular antichiral GPCs holding left- and right-propagating antichiral one-way edge states respectively, bidirectionally radiating one-way edge states at two parallel zigzag edges can be achieved. Our observations can enrich the understanding of fundamental physics and expand topological photonic applications.
Antichiral gyromagnetic photonic crystal (GPC) in a honeycomb lattice with the two interpenetrating triangular sublattices A and B magnetically biased in opposite directions can realize antichiral one-way edge states propagating along the same direction at its two parallel edges. Here, we report the construction and observation of topological beam splitting with the easily adjustable right-to-left ratio in an antichiral GPC. The splitter is compact and configurable, has high transmission efficiency, and allows for multi-channel utilization, crosstalk-proof, and robust against defects and obstacles. This magnificent performance is attributed to the peculiar property that antichiral one-way edge states exist only at zigzag edge but not at armchair edge of antichiral GPC. When we combine two rectangular antichiral GPCs holding left- and right-propagating antichiral one-way edge states respectively, bidirectionally radiating one-way edge states at two parallel zigzag edges can be achieved. Our observations can enrich the understanding of fundamental physics and expand topological photonic applications.
topological photonics one-way edge state photonic crystal beam splitting topological materials Opto-Electronic Science
2022, 1(5): 220001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
We present a discovery of an unusual unidirectionally rotating windmill scattering of electromagnetic waves by a magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder via an analytical theory for rigorous solution to fields and charges and an understanding of the underlying mathematical and physical mechanisms. Mathematically, the generation of nonzero off-diagonal components can break the symmetry of forward and backward scattering coefficients, producing unidirectional windmill scattering. Physically, this windmill scattering originates from the nonreciprocal unidirectional rotation of polarized magnetic charges on the surface of a magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder, which drives the scattering field to radiate outward in the radial direction and unidirectionally emit in the tangential direction. Interestingly, the unidirectional electromagnetic windmill scattering is insensitive to the excitation direction. Moreover, we also discuss the size dependence of unidirectional windmill scattering by calculating the scattering spectra of the gyromagnetic cylinder. These results are helpful for exploring and understanding novel interactions between electromagnetic waves and gyromagnetic materials or structures and offer deep insights for comprehending topological photonic states in gyromagnetic systems from the aspect of fundamental classical electrodynamics and electromagnetics.
unidirectional electromagnetic windmill scattering magnetized gyromagnetic cylinder topological photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(5): 053901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
![]()
![]() The Purcell effect is commonly used to increase the spontaneous emission rate by modifying the local environment of a light emitter. Here, we propose a silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna for simultaneously enhancing electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD) and electric quadrupole (EQ) emission. We study the scattering cross section, polarization charge distribution, and electromagnetic field distribution for electromagnetic plane wave illuminating the silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna, from which we have identified simultaneous existence of ED, MD and EQ resonance modes in this nanoantenna. We have calculated the Purcell factor of ED, MD and EQ emitters with different moment orientations as a function of radiation wavelength by placing these point radiation source within the nanoantenna, respectively. We find that the resonances wavelengths of the Purcell factor spectrum are matching with the resonance modes in the nanoantenna. Moreover, the maximum Purcell factor of these ED, MD and EQ emitters is 18, 150 and 118 respectively, occurring at the resonance wavelength of 475, 750, and 562 nm, respectively, all within the visible range. The polarization charge distribution features allow us to clarify the excitation and radiation of these resonance modes as the physical origin of large Purcell factor simultaneously occurring in this silicon cuboid nanoantenna. Our theoretical results might help to deeply explore and design the dielectric nanoantenna as an ideal candidate to enhance ED, MD and EQ emission simultaneously with very small loss in the visible range, which is superior than the more popular scheme of plasmonic nanoantenna.
The Purcell effect is commonly used to increase the spontaneous emission rate by modifying the local environment of a light emitter. Here, we propose a silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna for simultaneously enhancing electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD) and electric quadrupole (EQ) emission. We study the scattering cross section, polarization charge distribution, and electromagnetic field distribution for electromagnetic plane wave illuminating the silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna, from which we have identified simultaneous existence of ED, MD and EQ resonance modes in this nanoantenna. We have calculated the Purcell factor of ED, MD and EQ emitters with different moment orientations as a function of radiation wavelength by placing these point radiation source within the nanoantenna, respectively. We find that the resonances wavelengths of the Purcell factor spectrum are matching with the resonance modes in the nanoantenna. Moreover, the maximum Purcell factor of these ED, MD and EQ emitters is 18, 150 and 118 respectively, occurring at the resonance wavelength of 475, 750, and 562 nm, respectively, all within the visible range. The polarization charge distribution features allow us to clarify the excitation and radiation of these resonance modes as the physical origin of large Purcell factor simultaneously occurring in this silicon cuboid nanoantenna. Our theoretical results might help to deeply explore and design the dielectric nanoantenna as an ideal candidate to enhance ED, MD and EQ emission simultaneously with very small loss in the visible range, which is superior than the more popular scheme of plasmonic nanoantenna.
dielectric nanostructure spontaneous emission resonance Purcell effect Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(2): 210024
1 华南理工大学物理与光电学院, 广东 广州 510641
2 广东晶启激光科技有限公司, 广东 东莞 523808
拓扑光子态是具有单向传输特性的新型波导态,展示出抗背向散射、障碍物及缺陷免疫等独特而神奇的物理性质。拓扑光子态因其独特性在拓扑激光器、量子信息、混合集成光路、非线性光学等领域具有广泛的潜在应用。磁光光子晶体为实现拓扑光子态、探索拓扑光子态新物性提供了重要平台。本文聚焦磁光光子晶体中拓扑光子态的研究进展,首先回顾有序、无序晶格中的拓扑光子态,揭示拓扑光子态的微观物理图像。接着讨论时间和空间反演对称性双破缺体系中的拓扑光子态,简述反手性拓扑光子态的产生。然后介绍宽带拓扑光子态及拓扑慢光态研究,展示新颖的拓扑光学现象及器件设计。最后针对磁光光子晶体中拓扑光子态研究面临的关键问题、未来发展趋势进行分析和展望。
光学器件 磁光光子晶体 拓扑光子态 微观物理图像 器件设计
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, China
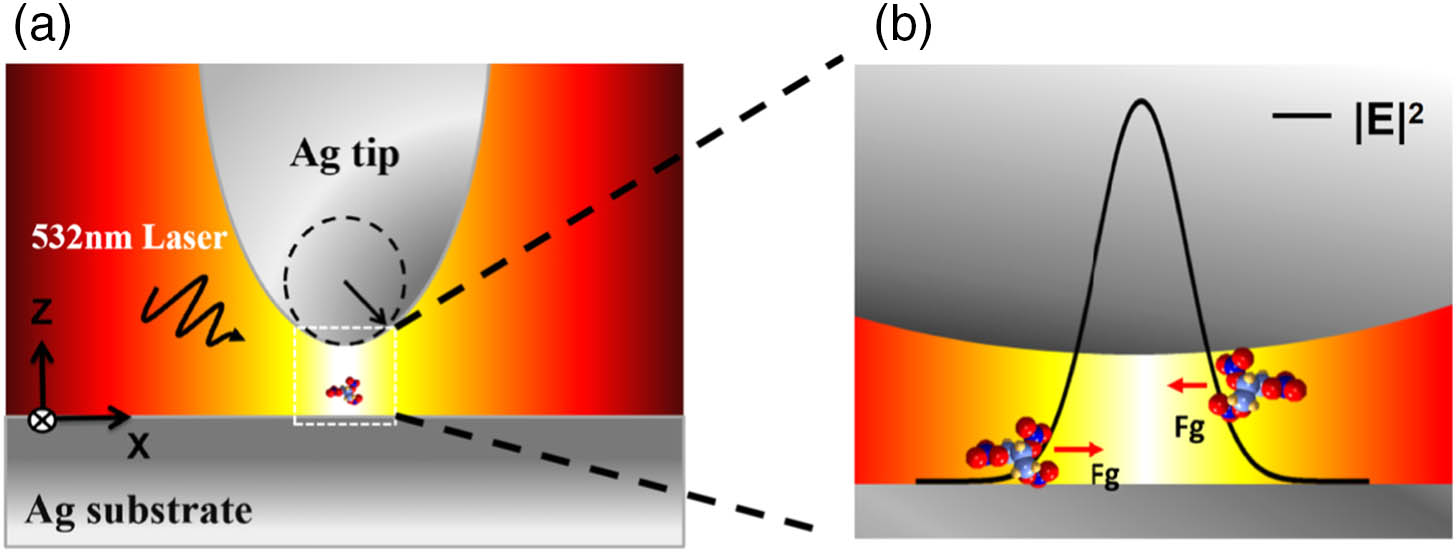
Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) offers a powerful means to enhance the Raman scattering signal of a molecule as the localized surface plasmonic resonance will induce a significant local electric field enhancement in the nanoscale hot spot located within the nanogap of the TERS system. In this work, we theoretically show that this nanoscale hot spot can also serve as powerful optical tweezers to tightly trap a molecule. We calculate and analyze the local electric field and field gradient distribution of this nanogap plasmon hot spot. Due to the highly localized electric field, a three-dimensional optical trap can form at the hot spot. Moreover, the optical energy density and optical force acting on a molecule can be greatly enhanced to a level far exceeding the conventional single laser beam optical tweezers. Calculations show that for a single organic molecule, which is modeled as a spherical molecule with a radius of , a dielectric coefficient , and a polarizability , the stiffness of the hot-spot trap can reach a high value of about and in the direction perpendicular and parallel to the TERS tip axis, which is far larger than the stiffness of single-beam tweezers, . This hard-stiffness will enable the molecules to be stably captured in the plasmon hot spot. Our results indicate that TERS can become a promising tool of optical tweezers for trapping a microscopic object like molecules while implementing Raman spectroscopic imaging and analysis at the same time.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(10): 10001573

Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, China
We design and present a switchable slow light rainbow trapping (SLRT) state in a strongly coupling topological photonic system made from a magneto-optical photonic crystal waveguide channel. The waveguide channel supports slow light states with extremely small group velocity (), low group-velocity dispersion, and a broadband operation bandwidth (3.60–4.48 GHz, near 22% of bandwidth). These slow light states originate from the strong coupling between two counter propagating topological photonic states. Under a gradient magnetic field, different frequency components of a wave packet are separated and stored at different positions for a long temporal duration with high spatial precision (without crosstalk and overlap between the electric fields of different frequencies) to form SLRT. Besides, these SLRT states can be easily switched among the forbidden state, trapped state, and releasing state by tuning the external magnetic field. The results suggest that the topological photonic state can offer a precise route of spatial-temporal-spectral control upon a light signal and find applications for optical buffers, broadband slow light systems, optical filters, wavelength-division multiplexing, and other optical communication devices.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(9): 09001075